wifidog认证实现OpenWRT强制认证的WIFI热点
首先安装wifidog到OpenWRT的路由器:
opkg update
opkg install wifidog
wifidog依赖下面这些模块:
iptables-mod-extra
iptables-mod-ipopt
kmod-ipt-nat
iptables-mod-nat-extra
libpthread
由于trunk的固件更新会比较频繁,会导致直接opkg install wifidog安装不了,如果你凑巧又没有备份与固件对应的Packages的话,就需要到http://downloads.openwrt.org/snapshots/trunk升级固件,然后再安装wifidog。
如果你的路由器不是openwrt官方支持的版本的话,那就需要自己编译固件。make menuconfig后,在Network–>Captive Portals中选择wifidog.
安装完成后,
/etc/init.d/wifidog enable
/etc/init.d/wifidog start
这时会抛出一个错误,因为我们还没有设置AuthServer的信息。关于安装wifidog更多的信息可以参考:http://wiki.openwrt.org/doc/howto/wireless.hotspot.wifidog
下面安装Auth Server,按照官方的说法:
AuthPuppy is the next generation authentication server for Wifidog networks.
源文档 http://www.authpuppy.org/
不过貌似这wifidog和Authpuppy都已经N久没更新了。。。
AuthPutty是需要安装apache2, php5和MySQL。详细介绍在这里:http://www.authpuppy.org/doc/Getting_Started (Windows版点这里)。
安装成功后,访问AuthPuppy会要求设置一些数据库信息,全部设置完成后能看到首页:

当然了,我们还需要设置管理员的账号。
进入Manage plugins,Install apAuthLocalUserPlugin,记得要enable这个插件。
然后,点击Manage Nodes,把默认节点的status改成deployed。这个GW(Gateway) ID default后面配置wifidog.conf的时候需要使用。
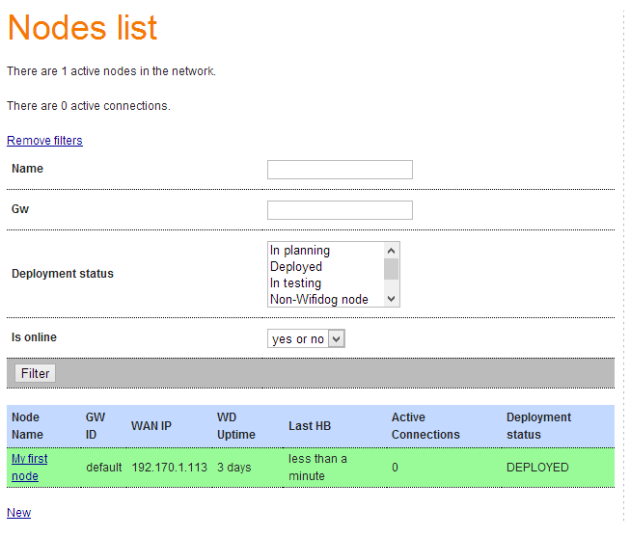
到这里,AuthPuppy就基本配置完毕了。
下面回到路由器,编辑wifidog.conf,一般情况下,我们之后配置ExternalInterface,GatewayInterface和AuthServer这三项就可以,其他默认。下面是我的配置:
GatewayIDdefault #注意这个ID必须跟AuthPuppy的GW ID一致
# Parameter: ExternalInterface
# Default: NONE
# Optional
#
# Set this to the external interface (the one going out to the Inernet or your larger LAN).
# Typically vlan1 for OpenWrt, and eth0 or ppp0 otherwise,
# Normally autodetected
ExternalInterface eth0 #路由器外网的物理接口
# Parameter: GatewayInterface
# Default: NONE
# Mandatory
#
# Set this to the internal interface (typically your wifi interface).
# Typically br-lan for OpenWrt, and eth1, wlan0, ath0, etc. otherwise
GatewayInterface wlan0 #路由器内网的物理接口
AuthServer {
Hostname 192.170.1.104
SSLAvailable no
Path /
}
CheckInterval 60
ClientTimeout 5
FirewallRuleSet global {
}
FirewallRuleSet validating-users {
FirewallRule allow to 0.0.0.0/0
}
FirewallRuleSet known-users {
FirewallRule allow to 0.0.0.0/0
}
FirewallRuleSet unknown-users {
FirewallRule allow udp port 53
FirewallRule allow tcp port 53
FirewallRule allow udp port 67
FirewallRule allow tcp port 67
}
FirewallRuleSet locked-users {
FirewallRule block to 0.0.0.0/0
}
注意这个Interface是物理接口。
root@OpenWrt:~# cat /etc/config/network
config interface ‘loopback’
option ifname ‘lo’
option proto ‘static’
option ipaddr ‘127.0.0.1’
option netmask ‘255.0.0.0’
config globals ‘globals’
option ula_prefix ‘fd09:fd03:490d::/48′
config interface ‘lan’
option proto ‘static’
option ipaddr ‘192.168.1.1’
option netmask ‘255.255.255.0’
option ip6assign ’60’
option _orig_ifname ‘eth0′
option _orig_bridge ‘false’
config interface ‘WAN’
option proto ‘dhcp’
option _orig_ifname ‘gretap0′
option _orig_bridge ‘false’
option ifname ‘eth0′
本文章由 http://www.wifidog.pro/2015/04/07/wifidog%E8%AE%A4%E8%AF%81wifi%E7%83%AD%E7%82%B9.html 整理编辑,转载请注明出处