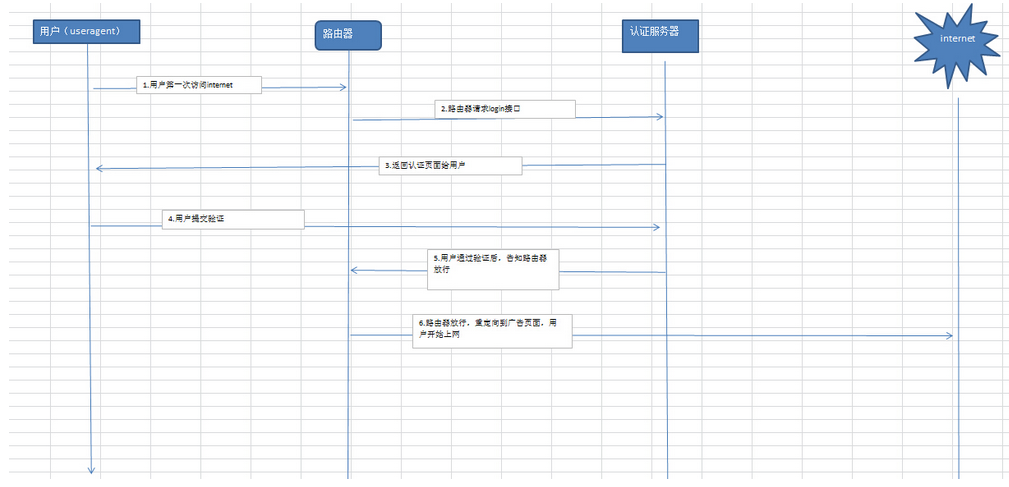
1. 系统需求
硬件
- 一台带有2个网络接口的计算机
- 一个无线AP设备(如,无线路由器)
软件
- Linux操作系统 (推荐ubuntu 8.04或更高)
- dhcp3-server
如果dhcp3-server还没有安装,你可以手动安装,例如,
在Debian中执行:
sudo apt-get install dhcp3-server
在Redhat/CentOS中执行:
yum install dhcp
将计算机的一个网络接口连接到Internet。
设置并启用无线网络,即用无线路由器创建一个可用Access Point。
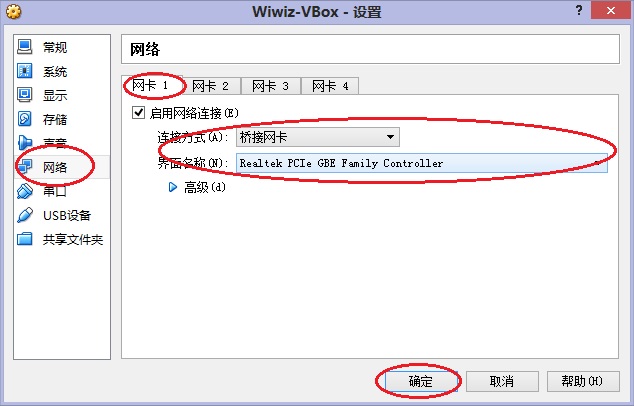
将另一个网络接口(有线的或无线的)连接到(或桥接到)你的无线AP设备以接入无线局域网(WLAN),并且手动设置一个IP。
建议清空iptables/防火墙设置。例如:
/etc/init.d/iptables stop
或
iptables -t nat -F
iptables -t filter -F
iptables -t mangle -F
注:
当所有的安装设置完成后,你的计算机(而不是无线AP)将充当无线网络的网关的角色。所以,如果你的无线AP设备是一个无线路由器,那么请禁用它的DHCP与UPNP服务。
2. 在Web控制面板中创建热点
登录到Web控制面板,访问http://cp.wiwiz.com/as/ 。
点击“我的热点”,在接下来的页面中点击“创建热点”。根据页面的提示完成各项设置,点击保存。
你将会看到你刚创建热点的Hotspot ID。记下它,接下来的步骤将会用到它。
3. 安装与设置Wiwiz HotSpot Builder Utility组件
从http://www.wiwiz.com/download/下载最新版的Wiwiz HotSpot Builder Utility。
执行以下命令进行安装:
cd / ; tar -zxf hsbuilder-util-latest.tar.gz
执行以下命令以开始设置:
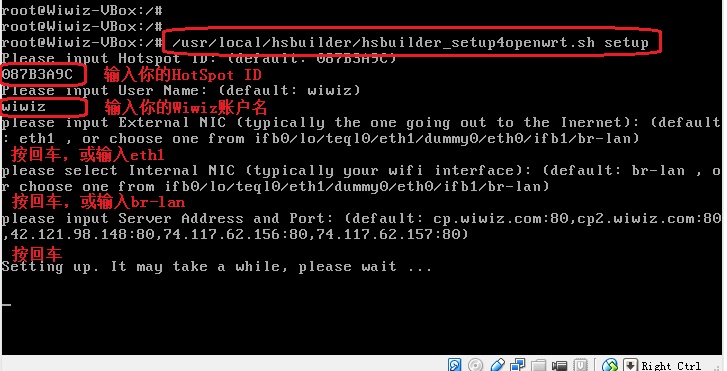
/usr/local/hsbuilder/hsbuilder_setup.sh setup
然后根据提示完成设置。
然后根据各步提示完成设置。以下是各步提示的说明:
“please select External NIC (typically the one going out to the Inernet):”– 此步请选择接入到Internet的网络接口。
“please select Internal NIC (typically your wifi interface):”– 此步请选择接入到局域网/无线局域网的网络接口。
“please input Hotspot ID:” — 此步请输入你在Wiwiz Web面板中创建的热点的Hotspot ID(不是热点的名称,也不是你的无线网络的SSID)。
“please input User Name:” — 此步请输入你的Wiwiz注册用户名。
“please input Server Address and Port:” — 此步请保持默认值。
“Do you want DHCP service to be configured? If you select No to skip it, you need to configure DHCP service manually later.” — 此步请选择是否让Wiwiz HotSpot Builder Utility自动配置DHCP服务。如果选择是,请继续以下的步骤。
“DHCP Setting: please input Network IP:” — 此步请输入你的局域网/无线局域网的网络IP。例如:192.168.1.0代表的是192.168.1.xxx网段。
“DHCP Setting: please input NET MASK:” — 此步请输入你的局域网/无线局域网的掩码。
“DHCP Setting: please input IP of Gateway (it should be the IP of this machine):” — 此步请输入今后的局域网/无线局域网的网关地址,即这台计算机的Internal NIC的IP地址(一般保留默认值即可)。
“DHCP Setting: please input DNS:” — 此步请输入DNS地址。默认值为程序自动检测到的DNS地址。也可以指定其他可用的DNS地址,推荐指定ISP提供的DNS地址。
“DHCP Setting: please input IP Range of this Network:” — 此步请输入DHCP地址分配范围。一般保留默认值即可。
最后,如果没有报错信息并看到“HSBuilder Setup Completed!”的提示文字,那么安装已经完成了。
注:
当上述过程完成后,如果程序提示警告信息“Warning: DHCP Service starting failed. You need to start it up manually.”,那么说明自动配置和启动DHCP服务失败,请自行手动配置并启动它。
你可以使用一个Wi-Fi客户端(如带WLAN适配器的PC或者支持Wi-Fi的移动电话)测试一下你的热点:
- 搜索可用Wi-Fi热点,并连接到你的热点。
- 打开Web浏览器,输入任何一个HTTP开头的网址。如果你的热点的认证页面能够显示出来,就说明你的热点已经正常运转了。
本文章由 http://www.wifidog.pro/2015/03/18/wifidog%E5%AE%89%E8%A3%85%E5%88%B0linux%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97%E6%9C%BA.html整理编辑,转载请注明出处