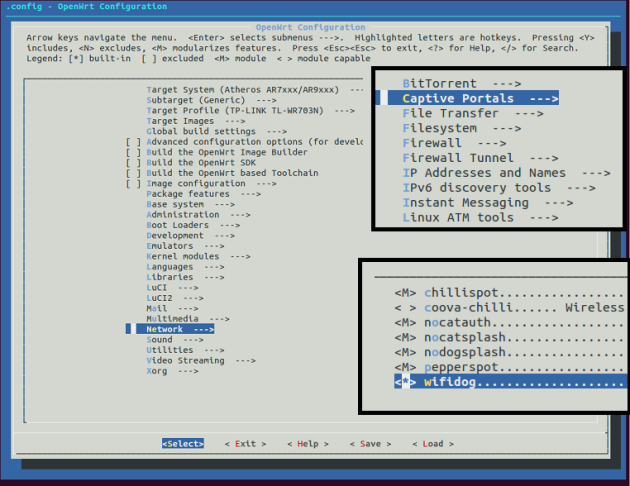
WiFidog编译成库
1) 在package/ utils下创建wifidog_lib目录。在wifidog_lib目录下创建一个文件夹src和一个Makefile文件。Makefile文件编写内容如下:
#
# Copyright (C) 2006,2013 OpenWrt.org
#
# This is free software, licensed under the GNU General Public License v2.
# See /LICENSE for more information.
#
include $(TOPDIR)/rules.mk
PKG_NAME:=wifidog_lib
PKG_VERSION:=20130917
PKG_BUILD_DIR := $(BUILD_DIR)/$(PKG_NAME)
include $(INCLUDE_DIR)/package.mk
define Package/wifidog_lib
SECTION:=utils
CATEGORY:=Utilities
DEPENDS:=+iptables-mod-extra +iptables-mod-ipopt +iptables-mod-nat-extra +libpthread
TITLE:=A wireless captive portal solution
endef
define Package/wifidog_lib/description
The Wifidog project is a complete and embeddable captive
portal solution for wireless community groups or individuals
who wish to open a free Hotspot while still preventing abuse
of their Internet connection.
endef
define Build/Prepare
mkdir -p $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)
$(CP) ./src/* $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/
endef
define Build/Configure
endef
define Build/Compile
$(MAKE) -C $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) \
CC="$(TARGET_CC)" \
CFLAGS="$(TARGET_CFLAGS) -Wall" \
LDFLAGS="$(TARGET_LDFLAGS)"
endef
define Package/wifidog_lib/conffiles
/etc/wifidog.conf
endef
define Package/wifidog_lib/install
$(INSTALL_DIR) $(1)/usr/bin
$(INSTALL_BIN) $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/test_wifidog $(1)/usr/bin/
$(INSTALL_DIR) $(1)/usr/lib
$(CP) $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/libwifidog.so* $(1)/usr/lib/
$(INSTALL_DIR) $(1)/etc
$(INSTALL_DATA) $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/wifidog.conf $(1)/etc/
endef
$(eval $(call BuildPackage,wifidog_lib))
2) 解压wifidog包进入src目录
tar xzvf wifidog-20130917-440445db60b0c3aff528ea703a828b0567293387.tar.gz –C src
3) 在src下创建Makefile文件,内容如下
LIB_VERMAJOR = 0
LIB_VERMINOR = 1
LIB_FILENAME = libhttpd.so
LIBWIFIDOG_FILENAME = libwifidog.so
OBJEXT = o
CFLAGS += -Os -pipe -mno-branch-likely -mips32r2 -mtune=34kc -fno-caller-saves -fhonour-copts -Wno-error=unused-but-set-variable -msoft-float
LIB_CFLAGS = $(CFLAGS) -shared -fPIC -DPIC
LIB_LDFLAGS = $(LDFLAGS) -Wl,-soname,$(LIB_FILENAME).$(LIB_VERMAJOR).$(LIB_VERMINOR)
LIBWIFIDOG_LDFLAGS = $(LDFLAGS) -Wl,-soname,$(LIBWIFIDOG_FILENAME).$(LIB_VERMAJOR).$(LIB_VERMINOR)
wifidog_OBJECTS = src/conf.$(OBJEXT) src/commandline.$(OBJEXT)\
src/debug.$(OBJEXT) src/fw_iptables.$(OBJEXT) src/firewall.$(OBJEXT) \
src/gateway.$(OBJEXT) src/centralserver.$(OBJEXT) src/http.$(OBJEXT) \
src/auth.$(OBJEXT) src/client_list.$(OBJEXT) src/util.$(OBJEXT) \
src/wdctl_thread.$(OBJEXT) src/ping_thread.$(OBJEXT) src/safe.$(OBJEXT) \
src/httpd_thread.$(OBJEXT) src/wifidogapi.$(OBJEXT)
wdctl_OBJECTS = src/wdctl.$(OBJEXT)
LIB_OBJ = libhttpd/protocol.o libhttpd/api.o libhttpd/version.o libhttpd/ip_acl.o
DEFS = -DHAVE_CONFIG_H
DEFAULT_INCLUDES = -I.-I..
sysconfdir = /etc
AM_CPPFLAGS += \
-I./libhttpd/ \
-DSYSCONFDIR='"$(sysconfdir)"'
COMPILE = $(CC) $(DEFS) $(DEFAULT_INCLUDES) $(INCLUDES) $(AM_CPPFLAGS) \
$(CPPFLAGS) $(AM_CFLAGS) $(CFLAGS)
LTCOMPILE = $(LIBTOOL) --tag=CC $(AM_LIBTOOLFLAGS) $(LIBTOOLFLAGS) \
--mode=compile $(CC) $(DEFS) $(DEFAULT_INCLUDES) $(INCLUDES) \
$(AM_CPPFLAGS) $(CPPFLAGS) $(AM_CFLAGS) $(CFLAGS)
CCLD = $(CC)
LINK = $(CCLD) $(AM_CFLAGS) $(CFLAGS) $(AM_LDFLAGS) \
$(LDFLAGS) -o $@
wifidog_LDADD = libhttpd/$(LIB_FILENAME).$(LIB_VERMAJOR).$(LIB_VERMINOR)
LIBS = -lnsl -lpthread
all: Makefile libhttpd libwifidog test_wifidog
test_wifidog: src/test_wifidog.o libhttpd libwifidog
@rm -f test_wifidog
$(LINK) src/test_wifidog.o $(LIBWIFIDOG_FILENAME).$(LIB_VERMAJOR).$(LIB_VERMINOR) $(LIBS)
wdctl: $(wdctl_OBJECTS) libhttpd
@rm -f wdctl
$(LINK) $(wdctl_OBJECTS) $(wdctl_LDADD) $(LIBS)
wifidog_test: $(wifidog_OBJECTS) libhttpd
@rm -f wifidog_test
$(LINK) $(wifidog_OBJECTS) $(wifidog_LDADD) $(LIBS)
libhttpd:$(LIB_OBJ) ./libhttpd/httpd_priv.h ./libhttpd/httpd.h
$(CC) $(LIB_CFLAGS) $(LIB_LDFLAGS) $(LIB_OBJ) $(LIBS) \
-o libhttpd/$(LIB_FILENAME).$(LIB_VERMAJOR).$(LIB_VERMINOR)
libwifidog:$(wifidog_OBJECTS) $(wdctl_OBJECTS) $(LIB_OBJ) ./libhttpd/httpd_priv.h ./libhttpd/httpd.h
$(CC) $(LIB_CFLAGS) $(LIBWIFIDOG_LDFLAGS) $(LIB_OBJ) $(wifidog_OBJECTS) $(wdctl_OBJECTS) $(LIBS) \
-o $(LIBWIFIDOG_FILENAME).$(LIB_VERMAJOR).$(LIB_VERMINOR)
.c.o:
$(CC) $(DEFS) $(AM_CPPFLAGS) $(DEFAULT_INCLUDES) $(INCLUDES) $(CFLAGS) -MD -fPIC -DPIC -c -o $@ $<
clean:
rm -f $(LIB_FILENAME)*
4) 修改src下对应的源代码,同时把scripts/init.d/wifidog脚本提供的功能通过lib库提供,这样 lib库需要提供int wifidogstart(),int wifidogstop(),int wifidogreload(),int wifidogrestart()。make package/wifidog_lib/compile V=s进行编译生成libwifidog.so.0.1和测试程序test_wifidog。
本文章由 http://www.wifidog.pro/2014/12/15/wifidog%E7%BC%96%E8%AF%91%E5%BA%93.html 整理编辑,转载请注明出处